On the Performance of Wireless Video Communication Using Iterative Joint Source Channel Decoding and Transmitter Diversity Gain Technique
Published In: Wireless Communications and Mobile Computing Impact Factor: 1.819
Abstract:
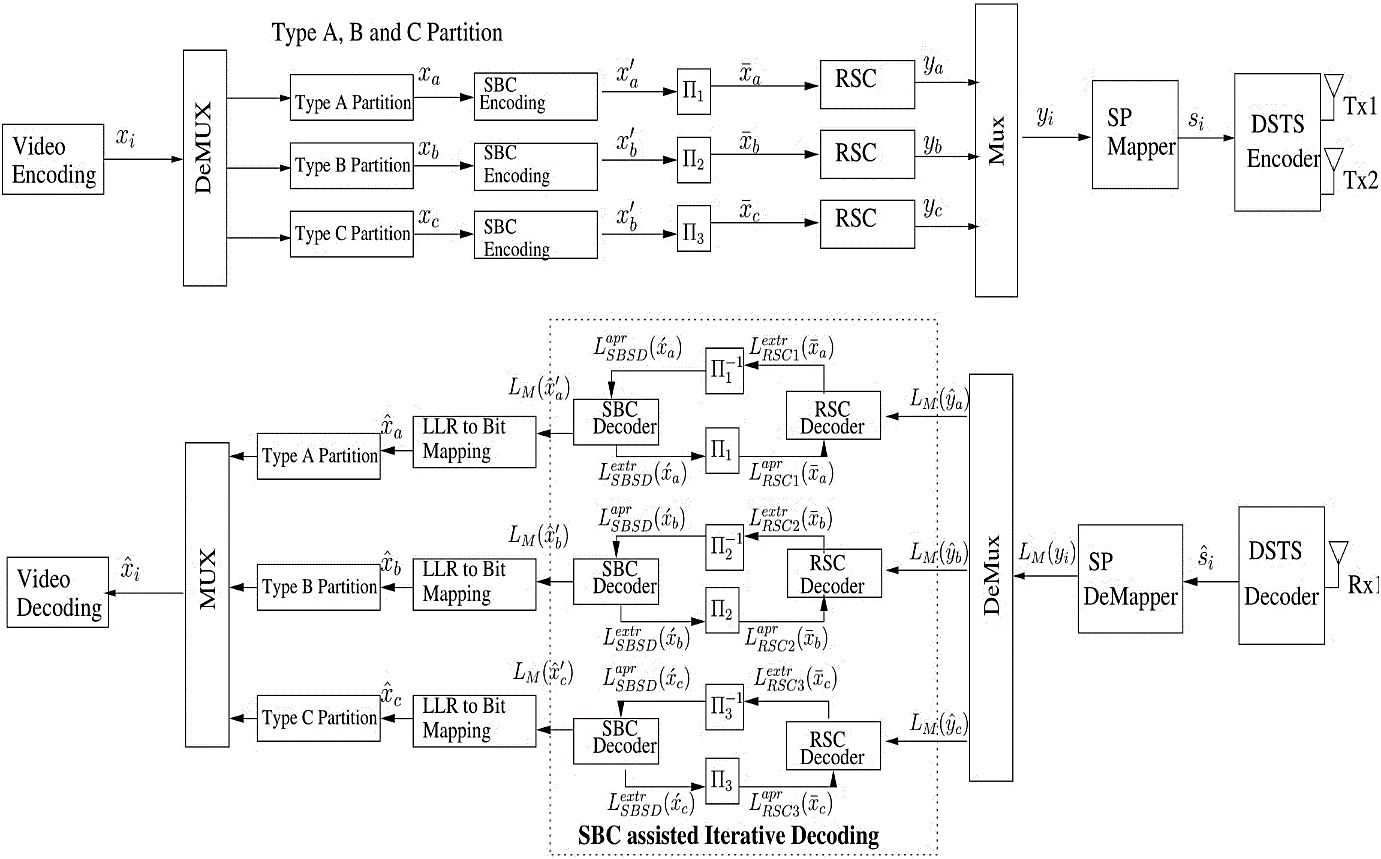
In this research work, we have presented an iterative joint source channel decoding- (IJSCD-) based wireless video communication system. The anticipated transmission system is using the sphere packing (SP) modulation assisted differential space-time spreading (DSTS) multiple input-multiple output (MIMO) scheme. SP modulation-aided DSTS transmission mechanism results in achieving high diversity gain by keeping the maximum possible Euclidean distance between the modulated symbols. Furthermore, the proposed DSTS scheme results in a low-complexity MIMO scheme, due to nonemployment of any channel estimation mechanism. Various combinations of source bit coding- (SBC-) aided IJSCD error protection scheme has been used, while considering their identical overall bit rate budget. Artificial redundancy is incorporated in the source-coded stream for the proposed SBC scheme. The motive of adding artificial redundancy is to increase the iterative decoding performance. The performance of diverse SBC schemes is investigated for identical overall code rate. SBC schemes are employed with different combinations of inner recursive systematic convolutional (RSC) codes and outer SBC codes. Furthermore, the convergence behaviour of the employed error protection schemes is investigated using extrinsic information transfer (EXIT) charts. The results of experiments show that our proposed Rate − 2/3 SBC-assisted error protection scheme with high redundancy incorporation and convergence capability gives better performance. The proposed Rate − 2/3 SBC gives about 1.5 dB Eb/N0 gain at the PSNR degradation point of 1 dB as compared to Rate − 6/7 SBC-assisted error protection scheme, while sustaining the overall bit rate budget. Furthermore, it is also concluded that the proposed Rate − 2/3 SBC-assisted scheme results in Eb/N0 gain of 24 dB at the PSNR degradation point of 1 dB with reference to Rate − 1 SBC benchmarker scheme.